Pen and paper are no longer necessary to sign employment contracts. Nevertheless, there are often still uncertainties regarding the use of eSignatures. Are electronic signatures legally valid? What laws and formal requirements must employers and personnel service providers observe? And what about data security? We clarify all open questions.
Basics of the eSignature
The eIDAS Regulation defines three categories of electronic signatures: simple, advanced and qualified electronic signatures. However, only the qualified electronic signature (QES) has the same probative value as a handwritten signature. Contracts signed with a QES are legally valid throughout the EU.
What is the difference between a digital and an electronic signature?
An electronic signature is a broad term for any electronic procedure that indicates consent to an agreement or record. It does not always include unique proof of identity. In addition, the term “electronic signature” is used in a legal context – as in the eIDAS Regulation.
Digital signatures are usually defined as a subtype of electronic signatures. They provide verified identity details of the signatory and guarantee the authenticity, integrity and forgery protection of the document. The QES has all of these properties and is therefore categorised as both an electronic and digital signature.
Employment contracts at a glance
The correct use of eSignatures depends on the type of employment contract to be signed. Firstly, a distinction can be made between open-ended and fixed-term contracts. The latter are divided into fixed-term contracts for a material reason (e.g. parental leave cover) and fixed-term contracts without a material reason. In Germany, however, fixed-term contracts without objective reasons are only permitted under certain conditions and for a period of up to two years.
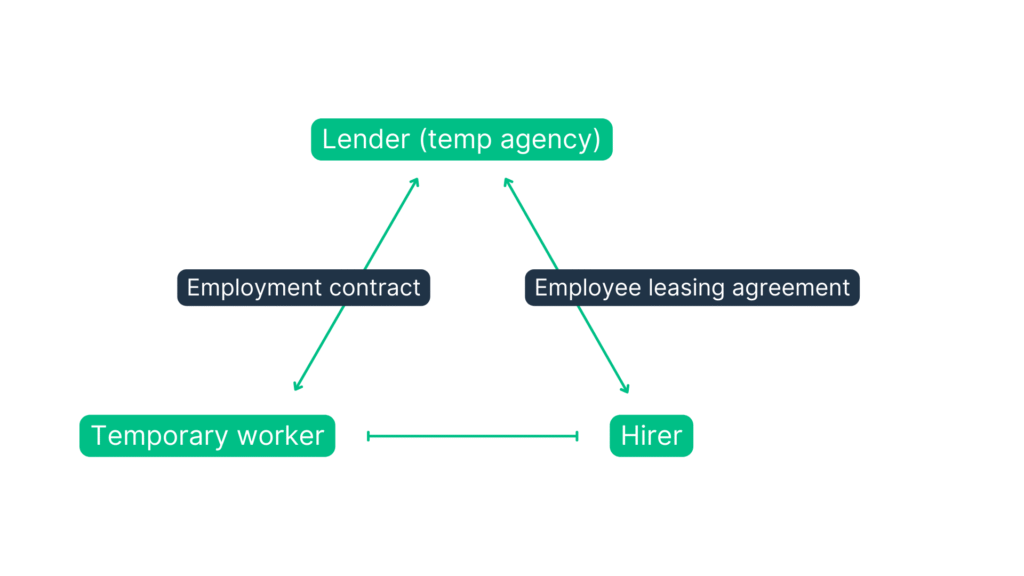
In the area of temporary employment (also known as temporary work or agency work), the contractual relationships are regulated separately. Here there is a triangular relationship, so to speak, between the hirer, the borrower and the temporary worker:
- The employee leasing agreement regulates the provision of labour between the lender (personnel service provider) and the hirer (company) for a fee, as well as the specific working conditions.
- An employment contract is concluded between the lender and the temporary worker. The lender remains the employer of the temporary worker during the loan phase.
- There is no direct employment relationship between the hirer and the temporary worker.
Temporary employment and labour contracts are necessary to create clarity for all parties involved. The legal framework is set out in the German Temporary Employment Act (AÜG).
Digital signature for employment contracts: Legal requirements
Evidence Act
In general, employment contracts are not subject to the written form requirement. However, there is an obligation to provide written proof of essential contractual conditions. Since the amendment to the Act on the Provision of Evidence (NachwG), employers must provide employees with additional information in writing. Depending on the type of information, this must be done on the first working day, after seven days or within one month. Electronic forms are not permitted. Therefore, if the employment contract is signed digitally, an additional document signed in writing must be submitted subsequently.
Specifications after time limit
In Germany, both permanent and fixed-term employment contracts can be signed electronically. As described above, the essential contractual conditions are also required in paper form. The following applies with regard to the type of signature:
– Open-ended employment contract: No formal requirements apply here. The qualified electronic signature (QES) is therefore not mandatory, but is nevertheless recommended due to its greater probative value.
– Fixed-term employment contract: The QES is mandatory here. Make sure that it is implemented correctly (both technically and legally), as an incorrectly signed fixed-term contract can be regarded as permanent.

Specifications by type of document
- The QES is always prescribed for temporary employment contracts.
- Cancellations of employment contracts are subject to the mandatory written form. Electronic form is excluded here in accordance with Section 623 BGB, i.e. an eSignature is explicitly not permitted. Written notice of termination must also be submitted if the employment contract is cancelled before the employee takes up the position.
Legislation also stipulates that employers must ensure that electronic signatures are understandable for employees and that the technology is implemented correctly.
Opportunities and risks of the eSignature
The advantages of the electronic signature are obvious: it reduces the administrative workload in HR departments, saves costs, enables faster onboarding and promotes environmental protection through less paper consumption. In addition, the QES offers full legal probative value when used correctly. Personnel service providers in particular benefit from this:
- Savings of up to €50 per mission
- accelerated contract conclusion: 90% of contracts are signed on the same day
- an increased occupancy rate
Concerns about electronic signatures usually relate to legal compliance and data security. This is because violations of legal requirements under labour law or the GDPR can result in high fines. If companies fail to comply with the obligation to provide evidence of the essential contractual conditions in accordance with the Evidence Act, they may face a fine of up to €2,000 and possibly even claims for damages. To avoid these risks, you should be familiar with the legal requirements for the employment contracts you use and fulfil them by using the correct eSignature standard – only the QES fulfils the written form requirement. You should also choose a software provider with high security standards to protect confidential information.
Obtain a digital signature: Which provider is the right one?
Electronic signatures are offered as a stand-alone solution or as part of more comprehensive software. For example, some HR tools offer the function to digitally sign the employment contract. The entire process – from creating the employment contract to sending, signing and saving – is then mapped in one tool. This option is very efficient, but more questionable in terms of data protection.
Pure eSigning solutions usually offer higher security. A provider such as Certifaction does not share contracts in the cloud and does not offer AI analysis, as this would allow access by third parties. So find out about data storage from your chosen provider. eIDAS compliance, certifications such as ISO 27001 and user-friendliness are other important decision criteria.
How the digital contract signing works
Upload the employment contract as a PDF in the tool and specify the desired signatories and settings. Certifaction can also be used to send several contracts to different signatories at the same time. HR managers and new employees receive an email in the desired order with a request for a signature.
The document can be viewed and digitally signed via the link provided – depending on the signature type, confirmation of the e-mail address, telephone number or identification using an ID document is required first. Proof of identity for the QES is usually provided online via video or auto-ident. Only then does the trust service provider issue the qualified certificate for the signature. The initiator is notified as soon as all signatures are available.
Conclusion
The digital signature of employment contracts is both legally recognised in Germany and the EU and can be implemented quickly. You should get an overview of the legal requirements in advance. After all, not all signatures are the same – in some cases, only the QES is valid. Whether you are a personnel service provider, start-up or multinational corporation, the electronic signature of employment contracts is relevant wherever companies want to take advantage of digitalisation.
Disclaimer: Legal requirements may change at any time. We do not guarantee the accuracy of the information provided.


